BARCODES vs QR CODES vs RFID
Table of Contents
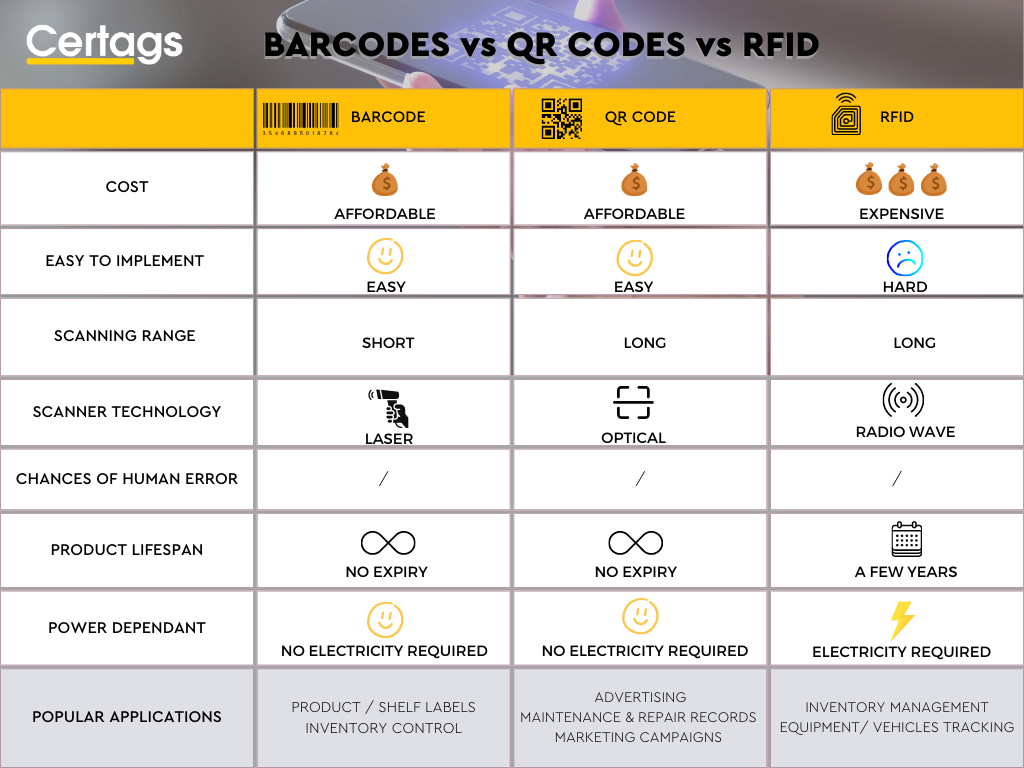
What are the differences?
When it comes to asset tracking and management, there are three leading technologies that businesses can choose from: barcodes, QR codes, and RFID. Each technology has advantages and disadvantages that every business needs to consider before implementation. Let’s see what barcodes, QR codes, and RFID are used for asset tracking and how they work together to make it easier than ever before to keep track of your assets.

Barcodes (1D Barcode)
Barcodes have been around for decades and are the most widely used technology for asset tracking due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of use. Barcodes require a physical scanner to read them, which makes them ideal for manual scanning processes but limits their ability regarding real-time data collection or automated processes like inventory management systems. Nevertheless, barcodes are an excellent tool for asset tracking, offering businesses the ability to track and manage their assets easily.
Advantages of barcode labels
- Cost-Effective: Barcodes offer an affordable way to track assets without having to invest in expensive RFID or GPS systems which can be costly upfront investments. Additionally, since most items already have existing barcodes (such as those found on consumer goods), it makes sense from a cost perspective to utilize these existing codes rather than invest in new ones made explicitly for asset tracking purposes.
- Accuracy and Efficiency: Barcode scanning is fast and accurate compared to manual data entry methods, such as typing information into spreadsheets or databases by hand. It may reduce errors that occur due to potential human error mistakes while inputting data manually. Implementing barcodes also helps streamline processes within organizations, leading to increased efficiency across departments/teams responsible for managing assets.
- Easy Integration With Current Systems: Many companies already use software programs, and barcodes integrate easily with various types of hardware. Scanners designed explicitly for reading coded labels (such as those found on products purchased at stores) – make it easy to implement barcoding solutions within current organizational structures.
Disadvantages of barcode labels
- Limited scanning range: as they are short-range applications (such as inventory management warehouses etc.), they cannot often accurately read further distances outside the warehouse environment where longer ranges might be necessary order capture signals sent out to devices located farther away from each other.
- Potential Data Loss: If scanned incorrectly, misread code results in incomplete, unreliable records, potentially leading to the loss of valuable information.
- Security Issues: Since all scanners share the same type of frequency signal, anyone nearby could pick up transmitted messages.
QR Codes (2D Barcodes)
QR codes have become a popular tool for asset tracking, allowing businesses to quickly and efficiently track their assets in real time.
QR codes provide a more dynamic solution than traditional barcode scanners since they allow users with smartphones or other devices equipped with cameras, to access information stored within the code without needing additional hardware equipment beyond the device itself.

Advantages of QR Codes
- Speed and accuracy with which they can collect data. Users can instantly access information about an item’s location and status without manually entering it into a database or other system by simply scanning the code with a smartphone or other device. This makes it much easier to keep tabs on inventory levels in warehouses or stores, ensuring items are always where they need to be when required by customers.
- Higher scanning range than standard barcodes (bi-directional scanning both horizontally and vertically)
- Can store more information than 1D barcodes
- Cost-Effective: no additional hardware must be purchased when QR Codes are implemented. You can print the labels containing the code from any printer connected to your computer network, and you’re good to go! Additionally, because these labels don’t require power sources like RFID tags do (which must use batteries), maintenance costs associated with keeping up your tagging system will remain low over time too.
Disadvantages of QR Codes
- Privacy and security risks: like barcodes, all kinds of information are stored within the label itself: customer information and more private security information can be scanned or hacked.
- Cost of scanners: depending on your business’ size, setting up multiple scanners throughout various locations can be costly due to installation/maintenance fees associated with each unit.
Incorporating QR technology into existing infrastructure provides several benefits outweighing the disadvantages listed above as long as proper precautions are taken during the implementation process.
RFID
RFID tags are fairly different in comparison to the barcode and QR Code. RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification, a type of wireless communication used to identify objects using radio waves.

Advantages of RFID
- Increased accuracy and speed: compared with other methods such as barcodes or manual counting systems. With an RFID system in place, you can quickly locate assets within seconds, no matter where they may be located onsite or offsite, without having to manually scan each item individually like you would have to do with a barcode system
- No fraud concerns: the tags attached to individual items contain unique identifiers that can’t be duplicated or copied by someone else. RFID eliminates any potential fraud concerns related to the misappropriation or theft of company assets while providing real-time data on inventory levels at all times.
Disadvantages of RFID
- Higher upfront costs: most systems require purchasing unique readers along with tags themselves.
- Compatibility issues between different brands/manufacturers which could lead to costly downtime during setup;
- Potential interference from other electronic devices operating nearby resulting inaccurate readings being taken by readers, thus leading to incorrect data being collected overall
- RFID implementation is time-consuming.
Barcodes vs QR Codes vs RFID: Which is better?
Barcodes and QR codes have revolutionised the way businesses track their assets. By utilising these simple yet powerful technologies, companies can quickly identify, locate and manage their inventory and equipment with unprecedented accuracy and efficiency. Compared to RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology, barcodes and QR codes offer several advantages that make them ideal solutions for asset tracking and management.
Barcodes and QR codes are cost-effective solutions for asset tracking compared to RFID tags which require additional hardware such as readers or antennas to function correctly. In addition, Barcode scanners are relatively inexpensive while still providing accurate data capture capabilities; similarly, scanning a quick response code is fast becoming an industry standard due to its affordability and ability to store large amounts of information in a tiny symbol.
In addition, anyone can easily print barcode labels on demand from any computer without having the specialised equipment you would need with RFID tags; making them more accessible to print in-house. For this reason they are more versatile when it comes the time to label new items or update existing ones within your system. Finally, unlike radio waves used by RFIDs which metal surfaces can block, light emitted from laser scanners used in reading 1D/2D symbols is not affected by physical obstructions; this ensures that all scanned items will always register even if they’re stacked close together inside boxes or containers.
Overall, using Barcodes and QR Codes provide greater benefits over other automated identification systems, such as Radio Frequency Identification (RFID). RFID offers some extra features, but many companies use it to do the same job as a barcode but at a higher price. Barcodes, for example, are best when you want one-to-one accuracy, while RFID is better for inventory applications. In addition, RFID asset tags can be very helpful when assets are not easily accessible, e.g. components within a sealed unit or where the location of the asset is only approximately known.
Which technology is right for me?
Both these technologies have their uses depending on the business and unique applications. Choosing the right one for you will be determined by your situation and various factors, which is why it is essential to understand the differences and special features.
Knowing what you want from your system is instrumental in making the right choice for your business.
Certags are experts in tag and label systems, automatic asset identification and tracking options. We would be happy to consult and advise you on the most efficient and cost-effective asset identification solution for your workplace, application and environment.
No matter the industry, we can provide a wide range of asset identification tags and label solutions that can be entirely customised according to your business needs.